| n | | Nano-. One billionth. |
| nerd | | A person with limited social, but advanced technological skills and interests.
|
| NetBench® | | A portable benchmark program from Ziff Davis Labs that measures how well a file server
handles file I/O requests from up to four different client types: DOS, 32-bit and 16-bit Windows, and/or Mac OS systems.
|
| NetWare | | A network operating system developed by Novell®, Inc.
|
| network | | An arrangement of objects that are interconnected. See LAN. Also, the transmission channels in communications which interconnect all client and server stations as well as all supporting hardware and software.
|
|
network adapter
| | An expansion card that connects a computer to the cables of a network and transmits the type of signals used throughout the network. On some computers, mainly portables, the adapter may be an external device, not a card.
|
|
network administrator
| | The person who manages the operation of a network, such as adding and removing user IDs, adding peripherals, and making backups of the data on the network.
|
| network architecture | | The entire structure of a network, including protocols, operating system, hardware, type of cabling, topology, interfaces, and adapter cards.
|
| network interface card. | | See
network adapter.
|
| network operating system | | An operating system able to handle the many tasks associated with a network, such as file locking, resource allocation, and error control.
|
| network server | | See
file server. |
| NFS | | Network File System. A method of allowing users to view drivers/directories on another computer as being on their computer.
|
| NIC | | Network Interface Card. See network adapter. |
| NiCad | | (nye-cad) Nickel-Cadmium. A rechargeable battery chemistry. Must be conditioned occasionally to retain its ability to receive a charge.
|
| NiMH | | Nickel Metal Hydride. A rechargeable battery chemistry. Does not have memory, and costs more than NiCad.
|
| node | | Any device visible to a network. A printer accessible by all stations on a network is a node, but a printer attached to one of the stations and usable only by that station is not a node. Literally, anywhere a connection occurs.
|
| non-interlaced | | Refers to monitors whose electron gun scans the entire screen without skipping any scan lines. Compare
interlaced. |
| nonmaskable interrupt | | An interrupt that cannot be disabled by another interrupt.
|
| non-parity memory | | Newer than parity and does not include the extra "error-detecting" chip.
|
|
nonvolatile
| | Does not disappear when the power is shut off, especially when referring to memory. Compare
volatile. |
| notebook computer | | A portable computer about the size of a piece of paper and usually less than two inches thick. Fits in an attaché case.
|
| ns | | Nanosecond. A billionth of a second. Used as a measure of RAM speed. Light travels not quite a foot in one nanosecond.
|
| NTSC | | National Television System Committee. Refers to the signals received and displayed in broadcast television.
|
| numeric keypad | | Number keys on the right of the keyboard arranged calculator-style, including the math operation keys.
|
| Num Lock key | | Short for numeric lock. A toggle key that switches the numeric keypad keys between their numeric function and arrow key functions.
|
| NVRAM | | Non- Volatile Random Access Memory. Uses either a permanently connected battery or takes advantage of non-volatile cache to store data indefinitely in the event of a power failure.
|
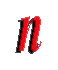 s
s![[Products]](/file/26092/MACD 5.bin/www/firmy/gateway/product_guide.gif)
![[Global Site]](/file/26092/MACD 5.bin/www/firmy/gateway/global_sites.gif)
![[Tech Support]](/file/26092/MACD 5.bin/www/firmy/gateway/tech_support.gif)
![[Corporate Information]](/file/26092/MACD 5.bin/www/firmy/gateway/corp_info.gif)
![[The Cow Zone]](/file/26092/MACD 5.bin/www/firmy/gateway/the_cow_zone.gif)
![[What's New]](/file/26092/MACD 5.bin/www/firmy/gateway/what's_new.gif)
![[Glossary]](/file/26092/MACD 5.bin/www/firmy/gateway/glossary.gif)
![[Search]](/file/26092/MACD 5.bin/www/firmy/gateway/search_engine.gif)
![[Home]](/file/26092/MACD 5.bin/www/firmy/gateway/home.gif)